Table of Contents
Recipient Types in Exchange 2016
There are multiple recipient types in exchange 2016 server.
If you navigate to recipients in the Exchange admin center. You will find the following list
- Mailbox
- Groups
- Resources
- Contacts
- Shared
- Migration
We will be discussing all the above recipient types in this article except migration.
Mailbox Types: Mailbox recipient has two category
a) User Mailbox
b) Linked Mailbox
a) User Mailbox: User mailbox is assigned to an active directory user.
Where the user manages his email send & receive, contacts, calendars, etc
User has rights on his mailbox.
If you create a new user mailbox on exchange server 2016.
An Active Directory user is already created.
And if you want to assign a user mailbox to an existing user in active directory.
Therefore, you will have to enable the user mailbox for a particular user to assign it.
b) Linked Mailbox: Linked Mailboxes are the mailbox where the user does not reside, where the exchange is deployed.
User accounts are located in a trusted forest.
The user account who access the linked mailbox does not exist in the forest, where the exchange server is present.
However, a disabled user account is created and linked with the linked mailbox.
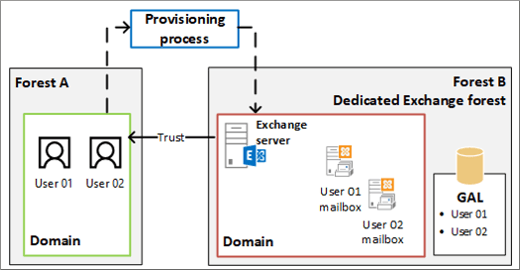
Note: There should be trust between exchange forest and the user account forest.
It can be a one-way outgoing trust
So that exchange forest may trust the account forest.
Groups Types In Exchange 2016: It has three category
a) Distribution Group
b) Security Group
c) Dynamic Distribution Group
a.1) Distribution Group: Its a universal distribution group in an active directory, which are mail-enabled.
Example: Instead of sending an email to every individual that belongs to a customer service group.
Therefore, it’s better to create a distribution group by the name of customer service and send an email to the group.
Finally, every member of the customer service group will receive an email
b.1) Security Group: It’s a mail-enabled universal security group object in an active directory.
This group can also use to distribute the message.
Moreover, this group can manage active directory resources access permissions as well.
c.1) Dynamic Distribution Group: Its a group whose membership depends on the filter basis.
It adds the user automatically to the group if matches the define attributes.
Example: If you want every user in a sales department to receive an email.
And users in a sales department changes often, It can be a headache to add or remove a user from the sales group.
Therefore, if you create a dynamic distribution group.
You can filter the users by their custom attributes like their department “sales”
Now every user having a custom attribute of sales will receive the email sent to a dynamic distribution group.
In addition, If a new user joins in a sales department and has the custom attribute of sales.
However, this new user will add automatically to the dynamic distribution group.
As a dynamic distribution group is calculated each time the message is sent.
Resources Types In Exchange 2016: It has Two category
a) Room Mailbox
b) Equipment Mailbox
a.1) Room Mailbox: These are the resources mailbox assigned to a physical location.
Such as a Training room or a conference hall.
An individual can easily reserve these rooms by including room mailbox in their meeting request.
b.1) Equipment Mailbox: It is also a resource mailbox but it is not location-specific.
Such as Projector, Laptop, Microphone, Company Car, etc
However, users can easily reserve these types of equipment by including the equipment mailbox in their meeting request.
Contacts: It has two category
a) Mail Contact
b) Mail User
a.1) Mail Contact: Basically its a contact for a person who does not belongs to an exchange organization.
Therefore, every mail contact does have an external email address.
Whenever an email is sent to this user, it will go to the external email address.
Also, a mail contact does not have any active directory user account.
b.1) Mail User: Mail user is also similar to a mail contact, it also has the external email address.
However, unlike a mail contact, a mail user has login access to active directory.
Therefore, mail user can log in to the active directory and can access the active directory resources.
Shared Mailboxes In exchange server 2016
Shared Mailbox: As the name appears, the shared mailbox is shared with multiple users.
These mailboxes are already in a way, where multiple users have access to them.
However, there is no login credential for these types of Mailboxes.
So, no can log on to this mailbox.
Therefore, they are assigned to the user who can access it.
Moreover, for Example, An email for customer service needs to be accessed by different users.
So, anyone can reply or take action on those emails.
However, by creating a shared mailbox by the name of customer service.
And assigning this mailbox to a different user can make the task easy for handling customer service emails.
Furthermore, you can watch the following video to know about recipient types in exchange 2016

For More Exchange Tutorial Videos, Visit Youtube Channel Techi Jack



